What is an antenna?
An antenna is a device that radiates electromagnetic waves into or receives them from space in a radio transceiver system. It is an essential part of a radio communication system.
An antenna is a converter that takes a guided wave propagating over a transmission line and converts it into an electromagnetic wave propagating in an unbounded medium (usually free space), or the reverse. A component used in radio equipment to transmit or receive electromagnetic waves. Engineering systems such as radio communications, radio, television, radar, navigation, electronic countermeasures, remote sensing, radio astronomy, and other engineering systems that utilize electromagnetic waves to transmit information rely on antennas to perform their work. In addition, in terms of transmitting energy with electromagnetic waves, non-signal energy radiation also requires antennas. General antennas are reversible, that is, the same antenna can be used as a transmitting antenna, can also be used as a receiving antenna. The basic characteristic parameters of the same antenna as transmitting or receiving are the same. This is the reciprocity theorem of antennas.
What is the role of antenna in high accuracy positioning?
GPS receiver performance is largely affected by the antenna technology, GPS antenna has four important parameters: Gain (Gain), Standing Wave (VSWR), Noise Factor (Noisefigure), Axial Ratio (Axialratio). Among them, Axialratio is especially emphasized, which is an important index to measure the difference in signal gain of the whole machine for different directions. Since satellites are randomly distributed on the hemispherical sky, it is very important to ensure that the antenna has similar sensitivity in all directions. The axial ratio is affected by the antenna performance, external structure, internal circuitry of the whole machine and EMI.
In the field of GNSS, high-precision antenna is a class of antenna that has special requirements for the stability of the antenna phase center, and it usually cooperates with high-precision boards to realize centimeter-level or millimeter-level high-precision positioning. In the design of high-precision antenna, the following indexes of the antenna usually have special requirements: antenna beamwidth, low elevation gain, out-of-roundness, roll-off coefficient, front-to-back ratio, and multipath resistance. All these indexes will directly or indirectly affect the phase center stability of the antenna, which in turn affects the positioning accuracy.
Types of high-precision antennas
Built-in GNSS Antenna
GNSS Active Antenna
(1) active antenna itself with LNA to improve the signal strength, the actual use of the antenna need to ensure that the radiating surface of the antenna toward the sky.
(2) metal devices around the antenna to be lower than the antenna radiator.
3)Square is right circular polarization, rectangle is linear polarization. If the structure allows, please try to use the square structure, in order to better receive satellite signals.
(4) The antenna connection line should be as short as possible, and it is better to use low-loss line.
(5) Note that the motherboard needs to be reserved for LNA power supply, and the impedance line at the end of the board needs to be reserved for isolation capacitors, power supply and impedance line need to be connected in series with more than 56nH inductance.
GNSS passive antenna
(1) The passive antenna needs the LNA on the main board to improve the signal strength, and the radiating surface of the antenna should be facing the sky in practical applications to ensure better reception performance.
2) The metal devices around the antenna should be lower than the antenna radiator.
3) Square is right circular polarization, rectangle is linear polarization. If the structure allows, please try to use square structure for better reception of satellite signals.
Picture
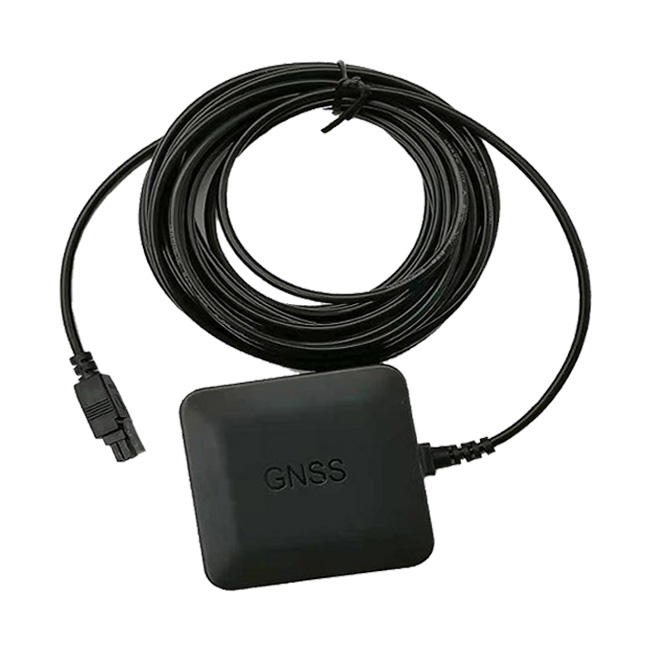
External GNSS antenna
1. Ensure that the antenna radiator is facing the sky when it is actually applied.
2, the antenna is placed as far as possible away from the area of high metal devices, to avoid blocking.
3、According to the actual need to choose the length of the antenna connection line, it is recommended to be as short as possible.
4, according to different modules to match the antenna built-in LNA gain size.
5, pay attention to the motherboard needs to be reserved for LNA power supply, and board impedance line needs to be reserved for isolation capacitors, power supply and impedance line need to be connected in series with more than 56nH inductance.
Basic Antenna Terminology
Gain (dBi): Under the same input power, the ratio of the antenna's radiated power at a certain point in space to the power of an ideal non-directional point source antenna at the same point, the unit of the gain is dBi, and the antenna manufacturers provide antenna test reports of the gain is generally in units of dBi.
Gain (dBd): In the same input power, the antenna in the space at a point of the radiated power and the ideal half-wave dipole antenna maximum radiation direction of the power ratio, the unit of the gain is dBd.
Express the same gain, expressed in dBi than expressed in dBd out to 2.15, that is, dBi = dBd + 2.15. For example: for an antenna with a gain of 0 dBd, its gain is converted into units of dBi, it is 2.15dBi.
Directivity: the ratio of the power generated by an antenna at a point in space to the power generated by an ideal non-directional point source antenna at the same point under the same radiated power.
Efficiency: The ratio of antenna radiated power to antenna input power.
APIP (Antenna Port Input Power): the amount of power added to the antenna port, is the amount of power output from the PA to the antenna port. This power is mainly related to the conducted transmit power of the mobile device.
EIRP (Effective Isotropic Radiated Power): Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power is the product of the power supplied to the antenna by the radio transmitter, Pt, and the absolute gain of the antenna, Gt, in a given direction, which reacts to the antenna's power in all directions.
EIRP represents the combined effect of the transmitted power Pt and the antenna gain Gt. EIRP is the power of a theoretically isotropic antenna (uniformly distributed in all directions) to produce the peak power density observed in the direction of maximum antenna gain. It is also referred to as the equivalent isotropic radiating power. EIRP can take into account transmission line and connector losses, including antenna gain.
PEIRP (Peak Effective Isotropic Radiated Power): Peak Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power.
ERP (Effective Radiated Power): The product of the power supplied to an antenna by a radio transmitter and the gain of that antenna with respect to a half-wave dipole in a given direction.
High Precision Antenna Applications and Classification
High-precision GNSS antenna was initially mainly used in the field of surveying and mapping, which was used to realize static millimeter-level positioning accuracy in the process of engineering sampling, topographic mapping and various control measurements. With the increasing maturity of high-precision positioning technology, high-precision antennas are gradually applied in more and more fields, including continuous operation reference station, deformation monitoring, seismic monitoring, measurement and mapping, unmanned aerial vehicles, precision agriculture, automatic driving field, driving test and training, engineering machinery and other industrial fields, and there are obvious differences in different applications of antenna index requirements.
1、CORS system, deformation monitoring, seismic monitoring-reference station antenna
High-precision antenna is used in continuous operation reference station, through long-term observation to obtain accurate position information, and through the data communication system real-time observation data transmission to the control center, the control center solves the error correction parameters in the region and then through the ground-based enhancement system, wide-area enhancement system, star-based enhancement system, etc., will be sent to the error information to the mobile station (the user), and ultimately the user to get the accurate coordinates. information. In applications such as deformation monitoring and earthquake monitoring, it is necessary to accurately monitor the amount of deformation and detect small deformations in order to predict the occurrence of natural disasters and so on.
Therefore, in the design of high-precision antennas for applications such as continuous operation reference stations, deformation monitoring, and seismic monitoring, the first thing that must be considered is their excellent phase center stability and resistance to multipath interference, so that they can provide accurate position information in real time for various enhancement systems. In addition, in order to provide as many satellite correction parameters as possible, the antenna must receive as many satellites as possible, and the four-system full-band has become the standard configuration. In such applications, the reference station antenna (base station antenna) covering the full frequency band of the four systems is usually used as the observation antenna of the system.
2、Measurement and Mapping-Built-in Measurement Antenna
In the field of surveying and mapping, it is necessary to design a built-in measurement antenna that is easy to integrate, and the antenna is usually built into the top of the RTK receiver to realize real-time high-precision positioning in the field of surveying and mapping.
The main considerations in the design of the built-in measurement antenna are frequency band coverage, beam coverage, phase center stability, antenna size, etc. Especially with the popularization of network RTK applications, the all-network built-in measurement antenna integrated with 4G, Bluetooth, WiFi gradually occupies a major share of the market, and it has been favored by a large number of RTK receiver manufacturers since it was launched in 2016, and it has been widely used to promote its application .
3、Driving test driving training, unmanned driving-external measurement antenna
The traditional driving test system has many drawbacks, such as large investment costs, high operation and maintenance costs, large impact by the environment, low accuracy, etc. After the application of high-precision antenna to the driving test system, the driving test system is transformed from manual judging to intelligent judging, with high judging accuracy, which greatly reduces the manpower and material costs of the driving test.
In recent years, the unmanned driving system has been developing rapidly, and in unmanned driving, the positioning technology of RTK high-precision positioning and inertial guidance combined positioning is usually adopted, which can realize high positioning accuracy in most environments.
In the driving test driver training, unmanned and other systems, often used in the form of external measurement antenna, the need for antennas with multi-system multi-frequency working band, can achieve high positioning accuracy, have a certain degree of suppression of multipath signals, as well as better environmental adaptability, can be used for a long time in outdoor environments without failure.
4、UAV-High precision UAV antenna
In recent years, the drone industry has been developing rapidly, and drones have been widely used in agricultural plant protection, surveying and mapping, electric power patrol and other scenarios, and in such scenarios, only equipped with a high-precision antenna can ensure the accuracy, efficiency and safety of various operations. As UAVs are characterized by fast speed, light load and short endurance, UAV high-precision antennas are designed to focus on factors such as weight, size, power consumption and to realize the broadband design as much as possible under the premise of ensuring weight and size.
5、Car intelligent antenna
Car can antenna products, including AM/FM, WIFI, BT, GPRS, GPS, 4G many types of antennas and wireless modules. The realized function is: the wireless communication module accepts the data and transmits it to the car host or the car navigation system through the Ethernet network, which realizes the communication and control between the car and the external wireless module.
6、Communication Antenna
Communication antenna, in our life is a very common communication equipment. But most people actually don't know much about it, they may just know that it can send and receive signals.
ST-35-AGH1 single-system dual-frequency external handheld antenna is mainly used for S-band handheld terminal communication, featuring small size, high gain and low power consumption. This series antenna has good performance of circular polarization, high gain in low elevation angle, stable performance, and can be used with many kinds of Beidou receivers.

Ltd. specializes in high-precision GNSS modules and wireless communication products, technology development and application promotion service providers, relying on the wireless communication technology in the field of R & D and promotion of experience, JUNODA set up a team with a wealth of experience in hardware and software development technology, aimed at domestic and foreign OEM / ODM customers and system integrators to provide high-quality, high-performance wireless modules and applications! We aim to provide high-quality, high-performance wireless modules and application programs to OEM/ODM customers and system integrators at home and abroad, and create long-term value for customers!
The company mainly provides integrated antenna module, dual-frequency high-precision module, single-frequency high-precision module, thousand-seeking high-precision module, Zhongke micro-positioning module, U-BLOX positioning module, SICOM communication module, inertial navigation DR module, UWM GNSS module, RTK differential module, 4G communication module and high-precision antenna, etc., the products are sold well in Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Guangdong, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Sichuan, Hunan and other parts of the country. Our GNSS modules are widely used in many application fields, such as drones, vehicle security monitoring and dispatching, automatic bus stop announcement, DVR, car DVD navigation, GPS electronic dog, synchronized timing, high-altitude balloon monitoring, engineering machinery, industrial automation, etc. In the field of wireless communication products, the company is closely involved in the field of wireless communication, such as RTK differential module, 4G communication module and high-precision antenna.
In the field of wireless communication products, the company follows the latest development of international communication technology, introduces and acts as an agent for wireless communication modules that meet the market demand, and the products have a comprehensive layout from 2G, 3G, 4G, and are widely used in financial electronic payment, vehicle remote control, remote advertising information, repeater monitoring, mobile Internet terminals, smart home, remote medical care, network testing, enterprise information management, anti-theft alarm, Remote video transmission, intelligent meter reading, mobile computing, network navigation, voice phone, wireless gateway and other fields. Focused areas include video surveillance, network optimization, routers, POS and other M2M industry applications.
If you need to consult, please contact online customer service!